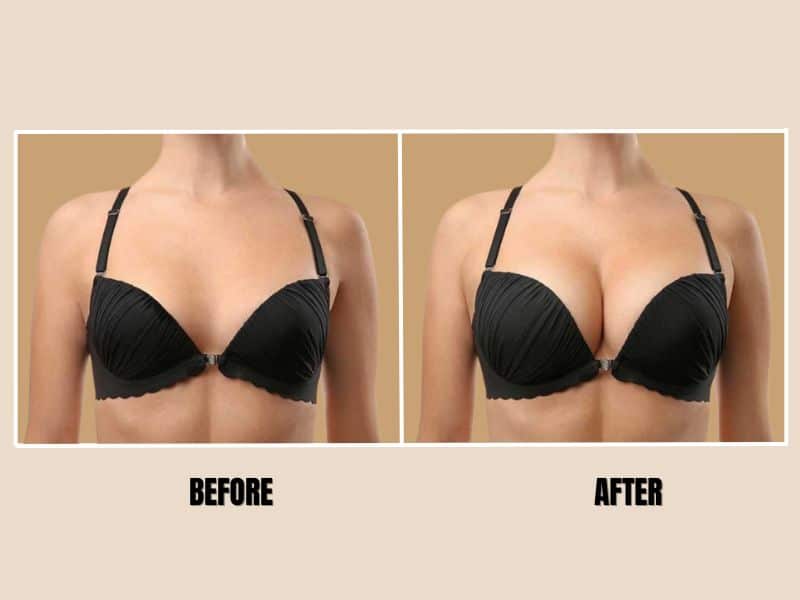
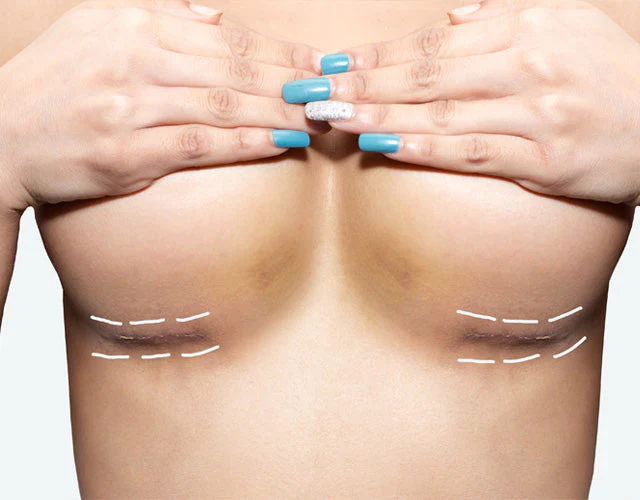
Mastopexy, commonly known as a breast lift, is a surgical procedure designed to raise and reshape sagging breasts (ptosis) by removing excess skin, tightening surrounding tissue, and repositioning the nipple-areolar complex to a more youthful position.
It restores breast firmness and contour without significantly altering breast size, though it can be combined with augmentation (implants) or reduction for desired volume. Mastopexy is one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries, with over 100,000 procedures performed annually in the U.S. alone, driven by factors like aging, pregnancy, weight fluctuations, and gravity. This article covers its history, indications, techniques, procedure, recovery, risks, and outcomes.
History and Evolution
The origins of breast lift surgery date back to the late 19th century, with early attempts to correct ptosis using skin excision. Significant advancements occurred in the 20th century:
- 1950s–1960s: Techniques focused on nipple transposition.
- 1970s: Introduction of the inverted-T (anchor) scar method.
- 1990s–2000s: Development of minimal-scar techniques like periareolar and vertical (lollipop) to reduce visible scarring.
- Modern era: Incorporation of auto-augmentation (using patient’s tissue), fat grafting, and internal mesh support for longer-lasting results.
Today, mastopexy often combines with implants for “augmentation-mastopexy,” addressing both sagging and volume loss.
Indications and Candidate Selection
Breast Sagging (ptosis) is graded by the Regnault classification:
- Mild: Nipple at inframammary fold.
- Moderate: Nipple below fold but above lowest breast contour.
- Severe: Nipple at lowest point.
Common causes: Pregnancy/breastfeeding, significant weight loss, aging, genetics.
Ideal candidates:
- Physically healthy, non-smokers.
- Stable weight.
- Realistic expectations.
- Completed childbearing (pregnancy can reverse results).
Not suitable for those planning major weight changes or future pregnancies.
Types of Mastopexy Techniques
Technique choice depends on ptosis degree, breast size, and desired scarring:
- Periareolar (Donut/Benelli): Circular incision around areola; for mild ptosis. Minimal scarring.
- Vertical (Lollipop): Around areola + vertical to fold; for moderate ptosis. Avoids horizontal scar.
- Inverted-T (Anchor/Wise Pattern): Around areola, vertical, and along fold; for severe ptosis/large breasts. Most comprehensive lift.
The Surgical Procedure
Performed under general anesthesia, lasting 2–4 hours as outpatient or overnight stay.
Steps:
- Incisions based on technique.
- Lift and reshape underlying tissue.
- Reposition nipple/areola higher.
- Remove excess skin.
- Close incisions (often with internal sutures for support).
If combined with augmentation, implants are placed simultaneously.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Immediate: Surgical bra, drains possible.
- First week: Rest, pain managed with medication; swelling/bruising peak.
- 2–6 weeks: Resume light activities; avoid strenuous exercise.
- Scars fade over 6–18 months.
Full results visible in 3–6 months as swelling subsides.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery:
- Scarring (permanent but fades).
- Infection, bleeding.
- Changes in nipple/breast sensation.
- Asymmetry, poor healing.
- Need for revision (10–15% cases).
Rare: Loss of nipple viability.
Advantages and Longevity
- Enhanced shape, confidence.
- Clothes fit better.
- Results last 10–15 years; gravity/aging may cause recurrence.
In summary, mastopexy is a safe, effective way to rejuvenate breast appearance with high satisfaction rates (>90%). Consult board-certified plastic surgeons for personalized assessment, reviewing before-after photos and discussing goals. Outcomes vary by individual anatomy and lifestyle.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/electric-brake-booster-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/composite-hoses-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/lavandula-oil-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/mabs-resin-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/eml-electro-absorption-modulated-laser-market